The Rain Alarm Project is a fantastic, simple solution that detects rain and alerts you with a buzzer or alarm. This project is perfect for anyone looking to automate tasks based on rain detection, like rainwater harvesting or adjusting home automation systems. In this blog, we’ll discuss the details of the Rain Alarm Project, from components to circuit diagrams, working principles, and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
The Rain Alarm Project is designed to detect rain and send an alert whenever the rain sensor detects moisture. This alert comes in the form of a buzzer, which triggers when the sensor identifies the presence of rain. This project proves to be beneficial in various fields such as agriculture, home automation, and automotive systems. By implementing the Rain Alarm Project, users can set up automatic responses based on rain detection, which contributes to saving water, improving farming efficiency, and increasing convenience in homes.
The Rain Alarm Project ensures that systems like irrigation and rainwater harvesting start operating only when it’s necessary, reducing wasted efforts. Furthermore, it can be integrated with vehicles to activate windshield wipers automatically or to send notifications for safety and convenience.
2. Objective
The main goal of the Rain Alarm Project is to design a system that detects rain and triggers an alert. When the rain sensor detects water droplets, it activates a circuit that produces a pulse, triggering the buzzer. This project can be used in various practical applications, including:
- Agriculture: To signal when rain occurs, initiating rainwater harvesting or irrigation systems.
- Automobiles: Automatically activating windshield wipers when rain is detected.
- Home Automation: Automating window operations or turning on rainwater collection systems.
In short, the Rain Alarm Project is designed to make our systems smarter and more responsive to the weather.
3. Components Used in the Rain Alarm Project
In order to build the Rain Alarm Project, several key components are needed. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper operation of the rain alarm system.
3.1 Rain Sensor
The rain sensor is the core component of the Rain Alarm Project. It detects the presence of rain and triggers the circuit. The rain sensor is designed using a Bakelite or Mica board with aluminum wires. When rain droplets hit the sensor, they create a conductive path between the contacts, completing the circuit and allowing the current to flow. This action is what sets the Rain Alarm Project in motion.
3.2 555 Timer IC
The 555 Timer IC is used in astable mode in this project. It generates a pulse signal whenever it’s triggered by the rain sensor. This pulse is then used to activate the buzzer. The 555 Timer IC controls how long the alarm will sound and ensures that the system works in a timely manner, providing a reliable output every time.
3.3 Transistors (BC548 and 2N2222)
Transistors play an important role in amplifying the signals within the Rain Alarm Project. The BC548 transistor amplifies the rain sensor’s signal, while the 2N2222 NPN transistors are used to trigger the 555 Timer IC. This amplification process ensures that the rain detection signal is strong enough to activate the alarm system effectively.
3.4 Buzzer
The buzzer is the audible alert of the Rain Alarm Project. Once the rain sensor is triggered and the 555 Timer IC generates a pulse, the buzzer is turned on. The buzzer stays on until the capacitors discharge, after which the alarm stops, ensuring that it alerts the user efficiently.
3.5 Resistors and Capacitors
The Rain Alarm Project uses various resistors and capacitors to manage the signal and timing of the system. For example, resistors ranging from 220Ω to 470KΩ help with signal conditioning, while capacitors ranging from 10nF to 100μF are used to stabilize the system and control the timing of the alarm’s activation and deactivation.
3.6 Diodes
In the Rain Alarm Project, a 1N4007 diode is used to protect the system from reverse currents. This protection ensures that the components, especially the 555 Timer IC, remain safe from potential damage caused by electrical surges.
3.7 Power Supply
The system runs on a 12V power supply, providing enough energy to operate the transistors, buzzer, and other components in the circuit. This ensures that the Rain Alarm Project functions reliably under all conditions.
4. Circuit Diagram of the Rain Alarm Project
Below is the circuit diagram of the Rain Alarm Project, which showcases the components connected to one another and the flow of current when rain is detected. The diagram illustrates how the rain sensor triggers the transistors, which in turn activate the 555 Timer IC to power the buzzer.
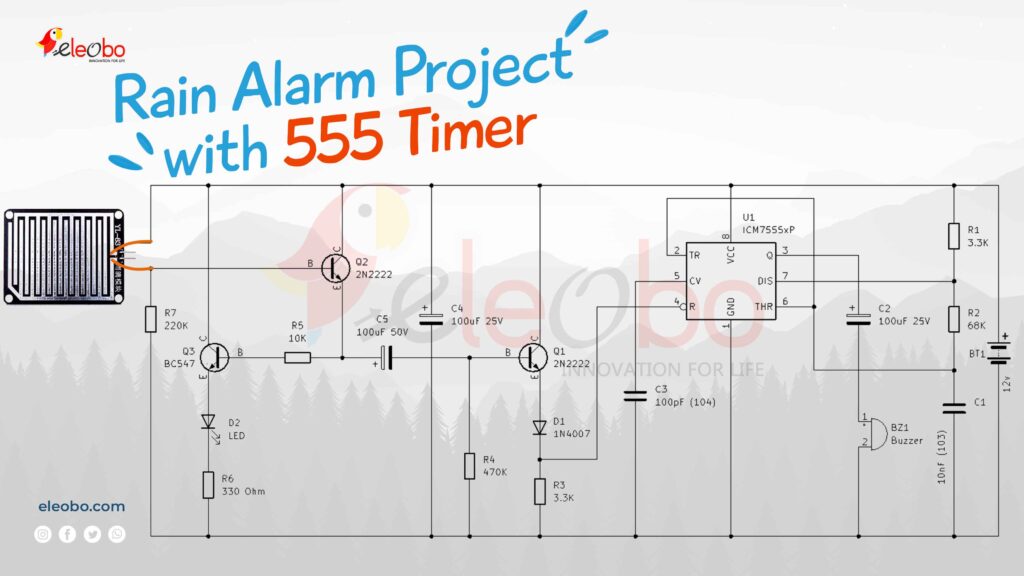
5. Working Principle of the Rain Alarm Project
5.1 Rain Sensor Activation
The rain sensor remains inactive in the absence of rain. However, once rain hits the sensor, it creates a conductive path between the contacts, reducing resistance. This allows the current to flow, activating the next stage of the circuit.
5.2 Triggering the Transistors
The rainwater sensor’s conductive path triggers Transistor Q2 (2N2222), which turns Transistor Q3 (BC548) on. This in turn powers the LED connected to Q3 and activates the next stage of the circuit.
5.3 555 Timer Activation
Once Transistor Q2 is triggered, Transistor Q1 is also turned on, which causes the Reset Pin of the 555 Timer IC to receive a positive voltage. This makes the 555 Timer active and generates a pulse signal at the output pin.
5.4 Alarm Activation
The pulse from the 555 Timer turns on the buzzer. The sound generated by the buzzer serves as the alarm. The system will keep the alarm activated until the capacitors discharge, resetting the 555 Timer. Once the capacitor is discharged, the alarm stops, and the system resets until the next rain detection.
5.5 Timing and Deactivation
The timing circuit, composed of resistors and capacitors, controls how long the buzzer will remain active. Once the capacitors discharge, the alarm turns off, and the Rain Alarm Project resets, ready to detect the next rainfall.
6. Applications of the Rain Alarm Project
The Rain Alarm Project has a wide range of practical applications, and here are some of the most common uses:
6.1 Agriculture
In agriculture, the Rain Alarm Project is incredibly useful. It can notify farmers when it starts raining, prompting them to activate rainwater harvesting systems or turn off irrigation systems to save water. This automated response helps optimize water usage in farming.
6.2 Home Automation
By integrating the Rain Alarm Project with home automation systems, homeowners can automatically close windows or activate rainwater collection systems whenever it rains. This integration helps protect homes and makes everyday tasks more convenient.
6.3 Automobiles
In automobiles, the Rain Alarm Project can be applied to automatically activate windshield wipers when rain is detected. This feature enhances driving safety by ensuring that wipers are activated as soon as they’re needed.
6.4 Communication Systems
In communication systems, the Rain Alarm Project can detect rainfall and boost antenna power, ensuring better signal quality during rainy weather. This helps prevent signal loss and improves communication reliability during storms.
6.5 Industrial Applications
Industries can use the Rain Alarm Project to detect adverse weather conditions like chemical rain or other environmental hazards. The system can alert workers to take appropriate actions and ensure safety measures are in place.
7. Conclusion
The Rain Alarm Project successfully detects rain and triggers an alert, making it an efficient and reliable solution for a variety of applications. By using affordable components like the 555 Timer IC, rain sensor, transistors, and buzzer, this project offers an excellent introduction to electronics while addressing real-world needs like rainwater harvesting and home automation.
7.1 Future Improvements
While the current Rain Alarm Project is effective, there are several areas for future improvement:
- Wireless integration: Enabling remote notifications about rain detection.
- Advanced sensors: Adding precision to rain detection.
- IoT integration: Connecting the system to the internet for data logging and automated control.
- Solar power: Making the system eco-friendly and energy-efficient.
By implementing these enhancements, we can further expand the capabilities of the Rain Alarm Project and contribute to better automation in homes, farms, and industries.
Download (PDF)
Download the complete Rain Alarm Project report in PDF format for more detailed explanations and diagrams!
Your download will start in 30 seconds.
By building the Rain Alarm Project, you can automate various systems and take timely actions based on real-time weather conditions. Stay ahead of the curve and make your environments smarter today!
Download BlueBot Controller App and start your journey today!
