In today’s world, safety and security are paramount. Protecting our valuables and property has become a necessity, and technology offers innovative solutions to achieve this. One such solution is the Laser Security Alarm Circuit, a simple yet highly effective project designed using easily available components. This project leverages the power of laser light to create a reliable security system that alerts you instantly when the laser beam is interrupted.
The Laser Security Alarm Circuit is not only cost-effective but also highly efficient. By using a BC548 transistor, this circuit ensures smooth operation and quick response. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a DIY enthusiast, this project is perfect for enhancing your home security. Let’s dive into the details of how this circuit works, the components required, and how you can build it yourself.
Table of Contents
Why Choose a Laser Security Alarm Circuit?
The Laser Security Alarm Circuit is a standout choice for security systems due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Laser light, known for its high strength and focused beam, acts as an invisible fence. When this beam is interrupted, the circuit triggers an alarm, alerting you immediately.
This project is particularly useful for securing doors, windows, or any entry points. The use of a BC548 transistor ensures that the circuit operates efficiently, making it a reliable choice for both beginners and experienced electronics enthusiasts.
Components Required for the Laser Security Alarm Circuit
To build the Laser Security Alarm Circuit, you’ll need the following components:
- NPN Transistor BC548 (2 pieces)
- LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)
- Buzzer
- LED (any color)
- Switch
- Resistor 100Ω (4 pieces)
- 9V Battery
- LASER Light Source
These components are easily available and affordable, making this project accessible to everyone.
How the Laser Security Alarm Circuit Works
The Laser Security Alarm Circuit operates on a simple principle. When the laser light falls on the LDR, the circuit remains inactive. However, when the laser beam is blocked, the circuit triggers an alarm. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
- LDR and Laser Light Interaction: The LDR is placed in the circuit to sense the laser light. When the laser light falls on the LDR, it offers low resistance, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
- Role of BC548 Transistors: Two BC548 transistors are used as switching devices in this circuit. The first transistor (Q2) receives voltage from the LDR. When the laser light is uninterrupted, Q2 remains ON, keeping the second transistor (Q1) OFF.
- Triggering the Alarm: When the laser light is blocked, the LDR’s resistance increases, cutting off the voltage supply to Q2. As a result, Q2 turns OFF, and Q1 turns ON. This activates the buzzer and LED, producing an audible alarm and visual indication.
Step-by-Step Construction Guide
Building the Laser Security Alarm Circuit is straightforward if you follow these steps:
Circuit Diagram
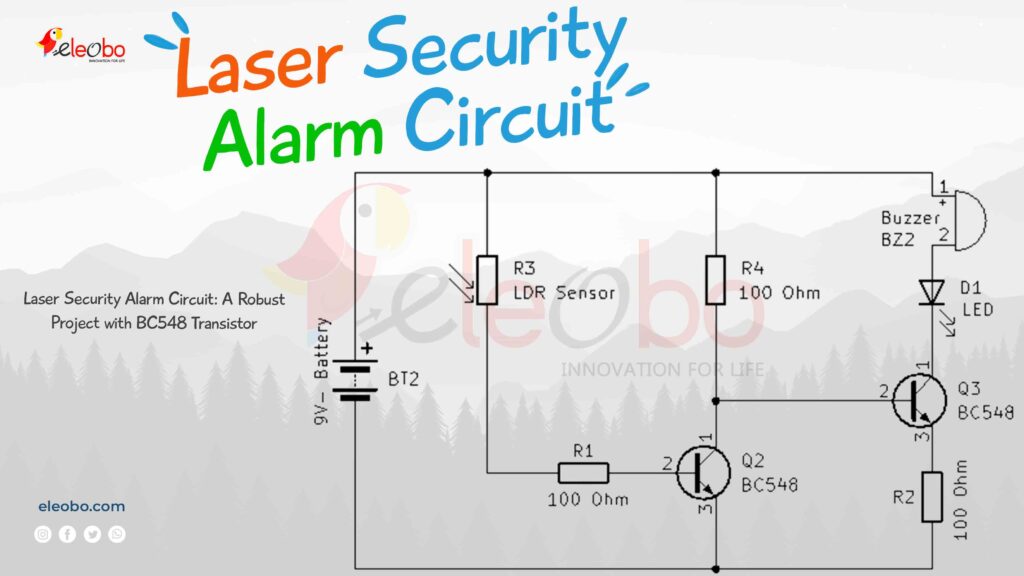
Circuit Components and Connections:
- LDR (Light Dependent Resistor): One end of the LDR is connected to the positive terminal (+9V) of the battery.
- The other end of the LDR is connected to a 100-ohm resistor (R1), and the other end of this resistor goes to the base of transistor Q2 (BC548).
- The collector of Q2 is connected to another 100-ohm resistor (R2), which is also connected to +9V.
- The collector of Q2 is also connected to the base of transistor Q3 (BC548).
- The emitter of Q2 is connected to the negative (-) terminal of the battery via a 100-ohm resistor (R3).
- The collector of Q3 is connected to the negative (-) terminal of the LED. The positive (+) terminal of the LED is connected to the negative (-) terminal of the buzzer.
- The positive (+) terminal of the buzzer is connected to the +9V battery terminal.
- The emitter of Q3 is connected to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
Download Laser Security Alarm Project Report
Here is a detailed project report on the Laser Security Alarm Circuit, which explains the working principle, components used, circuit design, and its applications. This project utilizes light-sensing technology with an LDR and laser beam to detect intrusions. When the laser beam is interrupted, the LDR’s resistance increases, activating transistor switching and triggering the alarm using an LED and buzzer. The circuit is simple, cost-effective, and highly reliable for security applications such as home security, bank lockers, military surveillance, and warehouse protection. Future enhancements may include microcontroller-based automation, remote alerts, and multiple sensor integration for improved efficiency.
Your download will start in 30 seconds.
Working of the Laser Security Alarm Circuit:
This circuit is based on an LDR and transistor switching mechanism. It works by detecting the presence or absence of laser light falling on the LDR.
Step-by-Step Working:
- When the laser beam is falling on the LDR:
- The LDR has a very low resistance (because light decreases LDR resistance).
- This creates a low voltage at the base of Q2 (transistor BC548).
- Since Q2 needs a higher base voltage to turn ON, it remains in the OFF state.
- Since Q2 is OFF, no current flows to Q3's base, keeping Q3 OFF as well.
- Since Q3 is OFF, the buzzer and LED remain OFF, meaning no alarm is triggered.
- When the laser beam is interrupted (Blocked):
- The LDR resistance increases (as it is now in darkness).
- This increases the voltage at the base of Q2, turning Q2 ON.
- When Q2 turns ON, current flows from collector to emitter, activating Q3.
- Since Q3 is ON, the circuit completes, allowing current to flow through LED and buzzer, activating them.
- The alarm (buzzer) starts ringing and the LED turns ON, indicating an intrusion.
Current Flow in the Circuit:
- Normal Condition (Laser ON, No Intruder):
- LDR has low resistance → base of Q2 gets low voltage → Q2 remains OFF.
- Q2 OFF → no current to Q3 base → Q3 remains OFF.
- No current flows through LED & buzzer → LED and buzzer remain OFF.
- Intruder Blocks the Laser:
- LDR resistance increases → base voltage of Q2 increases → Q2 turns ON.
- Q2 ON → current flows from collector to emitter → Q3 base gets activated.
- Q3 turns ON → current flows through LED and buzzer, turning them ON.
- The alarm is triggered, alerting an intrusion.
1. Electronic Components and Their Role
a) Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) - Light Sensor Technology
- An LDR (Photoresistor) is a light-sensitive component whose resistance decreases when exposed to light and increases in darkness.
- Used to detect whether the laser beam is present or blocked.
- Works based on the photoelectric effect (light changes material properties).
b) Transistor (BC548) - Switching and Amplification Technology
- The BC548 is an NPN transistor, which acts as a switch in this circuit.
- It has three terminals: Base (B), Collector (C), and Emitter (E).
- When a small current flows into the base, it allows a larger current to flow from collector to emitter, turning ON connected devices (LED, Buzzer).
- Works on the principle of current amplification.
c) Resistors - Current Control Technology
- Resistors limit and control current flow to prevent damage to components.
- They are used to set the correct biasing voltage for the transistor to function properly.
d) LED (Light Emitting Diode) - Visual Alert Technology
- LEDs emit light when forward biased (current flows through it).
- Acts as a visual indicator to show when the alarm is triggered.
e) Buzzer - Sound Alert Technology
- The buzzer produces sound when powered, providing an audible alert for security breaches.
f) 9V Battery - Power Source
- The circuit operates using a 9V DC battery, providing the necessary electrical energy to drive all components.
2. Basic Electronics Concepts Used
a) Ohm’s Law (V = IR)
- Defines the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R).
- Used to select the correct resistor values to control current flow in the circuit.
b) Photoconductivity
- The LDR works on the principle of photoconductivity, where its resistance changes based on light intensity.
- More light = low resistance → Less light = high resistance.
c) Transistor as a Switch
- The BC548 transistor is used as an electronic switch to turn ON/OFF the alarm system.
- When the base voltage reaches a threshold, the transistor switches ON, allowing current to flow.
d) Voltage Divider
- The LDR and resistor form a voltage divider circuit, generating a variable voltage based on the light intensity.
- This voltage determines whether the transistor turns ON or OFF.
e) Series and Parallel Circuit Design
- Series Circuit: The LED and buzzer are connected in series, so they turn ON together when activated.
- Parallel Circuit: The resistors and transistors form a parallel configuration to control switching effectively.
3. Technologies Integrated in the Circuit
a) Laser Technology
- A laser beam is used as an invisible light barrier.
- If the beam is interrupted, the circuit detects it and triggers the alarm.
b) Security Alarm System
- The combination of LDR, transistor, buzzer, and LED creates a basic security alarm system.
- Used in applications like door security, perimeter protection, and motion detection.
c) Low Power Electronics
- The circuit operates at low power (9V battery), making it energy-efficient.
- The transistors consume minimal current, ensuring long battery life.
d) Sensor-Based Automation
- The circuit functions automatically without manual intervention.
- LDR acts as an input sensor, detecting the presence or absence of light and controlling the alarm system.
Key Features of the Laser Security Alarm Circuit
- High Sensitivity: The LDR ensures that the circuit responds instantly to any interruption in the laser beam.
- Audible and Visual Alerts: The buzzer and LED provide both sound and light indications, making it easy to detect intrusions.
- Cost-Effective: The use of affordable components like the BC548 transistor makes this project budget-friendly.
- Easy to Build: With simple connections and minimal components, this circuit is perfect for beginners.
Precautions to Consider
While building and using the Laser Security Alarm Circuit, keep the following precautions in mind:
- Laser Safety: Laser light can be harmful to the eyes. Always handle the laser source with care and avoid direct exposure.
- Proper Alignment: Ensure the laser beam is accurately aligned with the LDR for optimal performance.
- Circuit Testing: Test the circuit thoroughly before deploying it for security purposes.
Applications of the Laser Security Alarm Circuit
The Laser Security Alarm Circuit has a wide range of applications, including:
- Home Security: Protect doors, windows, and other entry points from unauthorized access.
- Office Security: Secure valuable equipment and documents in your workplace.
- Industrial Use: Monitor restricted areas in factories or warehouses.
- Educational Projects: Use this circuit as a learning tool to understand basic electronics and security systems.
Enhancing the Circuit
For advanced users, the Laser Security Alarm Circuit can be enhanced by adding features like:
- Wireless Alerts: Integrate a GSM module to send alerts to your phone.
- Multiple Laser Beams: Use multiple laser sources and LDRs to cover larger areas.
- Solar Power: Replace the 9V battery with a solar panel for an eco-friendly power source.
Conclusion
The Laser Security Alarm Circuit is a powerful and reliable project that offers an excellent solution for safeguarding your property. By using a BC548 transistor, this circuit ensures efficient performance and quick response. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced electronics enthusiast, this project is a great way to enhance your skills while creating something truly useful.
So, why wait? Gather your components and start building your Laser Security Alarm Circuit today. With its simplicity, affordability, and effectiveness, this circuit is sure to provide the security you need.
- Download the BlueBot Controller App here.
- Make sure you have a Bluetooth-enabled smartphone to pair with your project.
Downlaod Basic electronics e-Book Click Here
Visit : Home Page
Learn about other sensors, such as Arduino sensors.
