Infrared (IR) technology has revolutionized the way we interact with the world around us. From remote controls to advanced security systems, IR infrared sensors play a pivotal role in modern technology. But how do IR infrared sensors work, and what makes them so effective? In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the science behind IR infrared sensors, explore their applications, and highlight why they are indispensable in today’s tech-driven world.
Table of Contents
What is an IR Infrared Sensor?
An IR infrared sensor is a device that detects infrared radiation emitted by objects. Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye. IR infrared sensors capture this radiation and convert it into an electrical signal, enabling various applications like motion detection, temperature measurement, and more.
The keyword here is IR infrared sensor, and understanding how it works is essential for appreciating its widespread use.
IR Sensor Working Principle
The working principle of an IR sensor revolves around detecting infrared radiation. All objects emit infrared energy as heat, and the sensor captures this energy using a photodiode or phototransistor. When infrared radiation hits the sensor, it generates an electrical signal proportional to the intensity of the radiation. This signal is then processed to determine the presence, distance, or temperature of an object.
For example, in a passive infrared (PIR) sensor, the device detects changes in infrared radiation within its field of view, making it ideal for motion detection. Understanding the IR sensor working principle is crucial for selecting the right sensor for your application.
IR Sensor Full Form
The full form of IR sensor is Infrared Sensor. The term “infrared” refers to the type of electromagnetic radiation the sensor detects, which lies just beyond the visible spectrum of light. Infrared radiation has wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves, making it ideal for applications like thermal imaging, remote controls, and proximity sensing.
Knowing the IR sensor full form helps clarify its purpose and functionality in various technologies.
IR Sensor Arduino Integration
Integrating an IR sensor with an Arduino opens up a world of possibilities for DIY projects and prototyping. The Arduino microcontroller can read the electrical signals from the IR sensor and use them to control other components like LEDs, motors, or displays. For instance, you can create a motion-activated light system or a line-following robot using an IR sensor and Arduino.
To connect an IR sensor to an Arduino, you typically need three pins: VCC (power), GND (ground), and OUT (signal). The Arduino reads the signal from the OUT pin and processes it using code written in the Arduino IDE. IR sensor Arduino projects are popular among hobbyists and educators due to their simplicity and versatility.
IR Sensor Pinout
Understanding the IR sensor pinout is essential for proper wiring and functionality. Most IR sensors have three pins:
- VCC: Connects to the power supply (usually 3.3V or 5V).
- GND: Connects to the ground.
- OUT: Provides the output signal to a microcontroller or other device.
Some IR sensors may have additional pins for features like adjustable sensitivity or onboard signal processing. Always refer to the datasheet of your specific IR sensor to ensure correct wiring and operation.
IR Sensor Use Cases
The use of IR sensors spans across various industries and applications. Here are some common examples:
- Home Security: IR sensors detect motion and trigger alarms or cameras.
- Automotive: Used in night vision systems and obstacle detection.
- Healthcare: Non-contact thermometers and pulse oximeters rely on IR sensors.
- Consumer Electronics: TV remotes and gaming consoles use IR sensors for wireless communication.
- Industrial Automation: IR sensors enable object detection, sorting, and quality control.
The versatility of IR sensor use makes them a vital component in modern technology.
IR Sensor Range
The range of an IR sensor depends on its type and design. Passive infrared (PIR) sensors typically have a range of up to 10 meters, making them suitable for motion detection in rooms or hallways. Active IR sensors, on the other hand, can have a range of several hundred meters, depending on the power of the infrared emitter and the sensitivity of the receiver.
When selecting an IR sensor, consider the required range for your application. For example, a security system may need a long-range sensor, while a home automation device may only require a short-range sensor.
The Science Behind How IR Infrared Sensors Work
To truly grasp how IR infrared sensors work, let’s break down the process step by step:
- Emission of Infrared Radiation:
All objects emit infrared radiation as a function of their temperature. The hotter the object, the more radiation it emits. IR infrared sensors are designed to detect this radiation. - Detection by the Sensor:
The IR infrared sensor contains a photodiode or phototransistor that is sensitive to infrared light. When infrared radiation hits the sensor, it generates an electrical charge. - Signal Processing:
The electrical signal produced by the sensor is then processed by a microcontroller or amplifier. This step is crucial because it converts raw data into actionable information. - Output and Application:
Finally, the processed signal is used to perform a specific function, such as triggering an alarm, adjusting a thermostat, or even controlling a robotic device.
By understanding how IR infrared sensors work, we can appreciate their versatility and efficiency in various applications.
Types of IR Infrared Sensors
IR infrared sensors come in different types, each designed for specific purposes. Here are the most common ones:
- Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors:
PIR sensors detect changes in infrared radiation within their field of view. They are commonly used in motion detectors and security systems. - Active Infrared Sensors:
These sensors emit infrared radiation and detect the reflection from objects. They are often used in obstacle detection and distance measurement. - Thermal Infrared Sensors:
Thermal sensors measure the temperature of objects by detecting the intensity of infrared radiation. They are widely used in medical imaging and industrial applications. - Reflective Infrared Sensors:
These sensors work by emitting infrared light and measuring the amount reflected back. They are commonly found in line-following robots and automation systems.
Each type of IR infrared sensor has unique features, making them suitable for different tasks.
Applications of IR Infrared Sensors
The versatility of IR infrared sensors makes them indispensable in various industries. Here are some key applications:
- Home Automation:
IR infrared sensors are used in smart home devices like automatic lights, security cameras, and climate control systems. - Healthcare:
In medical devices, IR infrared sensors enable non-contact temperature measurement and blood oxygen level monitoring. - Automotive Industry:
Modern vehicles use IR infrared sensors for night vision, obstacle detection, and driver assistance systems. - Industrial Automation:
Factories rely on IR infrared sensors for quality control, temperature monitoring, and robotic guidance. - Consumer Electronics:
From TV remote controls to gaming consoles, IR infrared sensors enhance user experience by enabling wireless communication.
The widespread use of IR infrared sensors highlights their importance in our daily lives.
Advantages of IR Infrared Sensors
Why are IR infrared sensors so popular? Here are some of their key benefits:
- Non-Contact Operation:
IR infrared sensors can detect objects without physical contact, making them ideal for delicate or hazardous environments. - High Accuracy:
These sensors provide precise measurements, ensuring reliable performance in critical applications. - Energy Efficiency:
IR infrared sensors consume minimal power, making them suitable for battery-operated devices. - Durability:
With no moving parts, IR infrared sensors are highly durable and require minimal maintenance. - Versatility:
From simple remote controls to complex industrial systems, IR infrared sensors adapt to a wide range of applications.
These advantages make IR infrared sensors a preferred choice for engineers and designers worldwide.
How to Choose the Right IR Infrared Sensor
Selecting the right IR infrared sensor depends on your specific needs. Here are some factors to consider:
- Detection Range:
Choose a sensor with a range that matches your application. For example, security systems require long-range detection, while home automation devices may need shorter ranges. - Sensitivity:
Higher sensitivity ensures accurate detection, especially in low-light conditions. - Response Time:
Faster response times are crucial for applications like motion detection and robotics. - Environmental Conditions:
Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and interference when selecting a sensor. - Cost:
Balance performance with budget to find the best solution for your needs.
By evaluating these factors, you can choose the perfect IR infrared sensor for your project.
Arduino IR Sensor Test Code with 2 LEDs
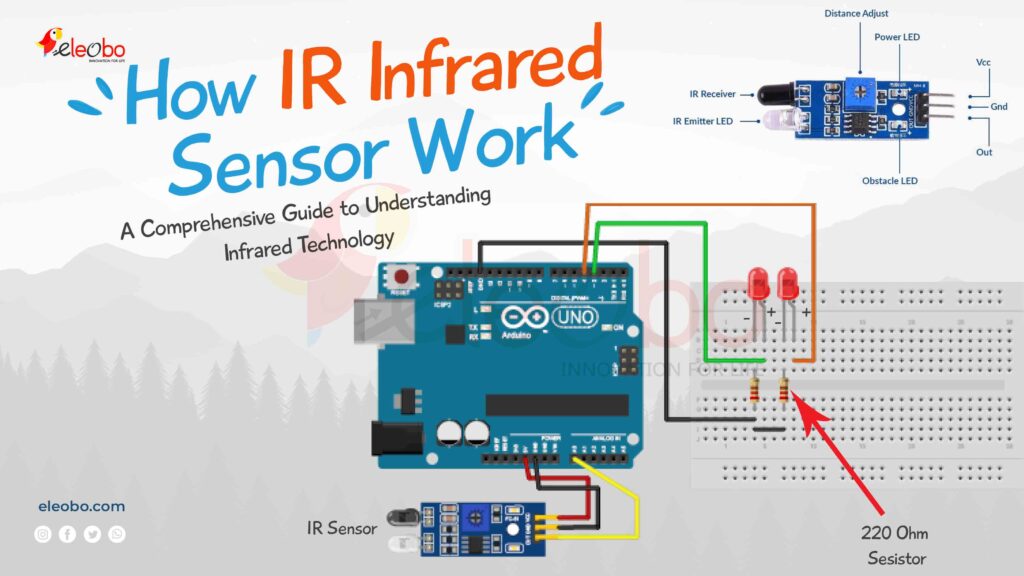
To demonstrate how an IR sensor works with an Arduino, let’s create a simple project that reads both analog and digital signals from the sensor and controls two LEDs based on the readings.
Components Needed:
- Arduino Uno
- IR sensor (digital or analog)
- 2 LEDs (e.g., one red and one green)
- 2 resistors (220Ω for LEDs)
- Breadboard and jumper wires
Wiring Diagram:
- Connect the VCC pin of the IR sensor to 5V on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the IR sensor to GND on the Arduino.
- Connect the OUT pin of the IR sensor to a digital pin (e.g., D2) or analog pin (e.g., A0) on the Arduino.
- Connect the anode (long leg) of the first LED to a digital pin (e.g., D3) and the cathode (short leg) to GND via a 220Ω resistor.
- Connect the anode of the second LED to another digital pin (e.g., D4) and the cathode to GND via a 220Ω resistor.
Arduino Code:
// Define pin numbers
const int irSensorPin = A0; // Use A0 for analog or D2 for digital
const int ledPin1 = 3; // First LED pin
const int ledPin2 = 4; // Second LED pin
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set LED pins as output
pinMode(ledPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Read the sensor value
int sensorValue = analogRead(irSensorPin); // Use digitalRead() for digital sensors
// Print the sensor value to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
// Control LEDs based on sensor value
if (sensorValue > 500) { // Adjust threshold based on your sensor
digitalWrite(ledPin1, HIGH); // Turn on first LED
digitalWrite(ledPin2, LOW); // Turn off second LED
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin1, LOW); // Turn off first LED
digitalWrite(ledPin2, HIGH); // Turn on second LED
}
// Add a small delay for stability
delay(100);
}How It Works:
- The IR sensor detects infrared radiation and sends a signal to the Arduino.
- The Arduino reads the signal (analog or digital) and prints the value to the serial monitor.
- Based on the sensor value, the Arduino turns on one LED and turns off the other. For example, if the sensor detects an object (high value), LED 1 turns on, and LED 2 turns off. If no object is detected (low value), LED 2 turns on, and LED 1 turns off.
This simple project demonstrates how to use an IR sensor with an Arduino and control LEDs based on sensor readings.
Conclusion
Understanding how IR infrared sensors work is essential for leveraging their full potential. From their scientific principles to their diverse applications, IR infrared sensors are a cornerstone of modern technology. Whether you’re designing a smart home system, developing a medical device, or exploring industrial automation, IR infrared sensors offer unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and versatility.
By staying informed about the latest trends and advancements, you can harness the power of IR infrared sensors to create innovative solutions for a better tomorrow.
- Download the BlueBot Controller App here.
- Make sure you have a Bluetooth-enabled smartphone to pair with your project.
Downlaod Basic electronics e-Book Click Here
Visit : Home Page
Learn about other sensors, such as Arduino sensors.
